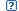
ORF7a protein [Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2]
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| ORF7a_SARS-CoV-2-like | cd21684 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) structural accessory protein ... |
1-121 | 3.78e-74 | |||
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) structural accessory protein ORF7a and a bat coronavirus (BatCoV RaTG13) from related betacoronaviruses in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (B lineage); This group contains the structural accessory protein ORF7a, also called NS7a, of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronaviruses (SARS-CoV) from betacoronavirus subgenera Sarbecovirus (lineage B), including SARS-CoV-2, also known as 2019-nCoV, and a bat coronavirus (BatCoV RaTG13), which was previously detected in Rhinolophus affinis from China's Yunnan province. ORF7a/NS7a from betacoronavirus in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (B lineage) are not related to NS7a proteins from other coronavirus lineages. There are five essential genes in CoVs that result in the following gene products: Spike (S) protein, Membrane (M) glycoprotein, Nucleocapsid (N), Envelope (E) protein, and the ORF1ab (a large polyprotein known as replicase/protease); all required to produce a structurally complete viral particle. In addition, SARS-CoV contains a number of open reading frames that code for a total of eight accessory proteins, namely ORFs 3a, 3b, 6, 7a, 7b, 8a, 8b, and 9b. These ORFs are specific for SARS-CoV and do not show significant homology to accessory proteins of other coronaviruses. Structurally, ORF7a possesses a distinctive immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain which is related to extracellular metazoan Ig domains that are involved in adhesion, such as ICAM; it also contains a 15-aa signal peptide sequence at its N terminus, an 81-aa luminal domain, a 21-aa transmembrane domain, and a short C-terminal tail. Coexpression of SARS-CoV ORF7a with S, M, N, and E proteins resulted in production of virus-like particles (VLPs) carrying ORF7a protein, indicating that ORF7a is a viral structural protein. Expression studies of ORF7a have shown that biological functions include induction of apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway, activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, inhibition of host protein translation, and suppression of cell growth progression. These results collectively suggested that ORF7a protein may be involved in virus-host interactions. : Pssm-ID: 394935 Cd Length: 121 Bit Score: 216.04 E-value: 3.78e-74
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| ORF7a_SARS-CoV-2-like | cd21684 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) structural accessory protein ... |
1-121 | 3.78e-74 | |||
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) structural accessory protein ORF7a and a bat coronavirus (BatCoV RaTG13) from related betacoronaviruses in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (B lineage); This group contains the structural accessory protein ORF7a, also called NS7a, of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronaviruses (SARS-CoV) from betacoronavirus subgenera Sarbecovirus (lineage B), including SARS-CoV-2, also known as 2019-nCoV, and a bat coronavirus (BatCoV RaTG13), which was previously detected in Rhinolophus affinis from China's Yunnan province. ORF7a/NS7a from betacoronavirus in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (B lineage) are not related to NS7a proteins from other coronavirus lineages. There are five essential genes in CoVs that result in the following gene products: Spike (S) protein, Membrane (M) glycoprotein, Nucleocapsid (N), Envelope (E) protein, and the ORF1ab (a large polyprotein known as replicase/protease); all required to produce a structurally complete viral particle. In addition, SARS-CoV contains a number of open reading frames that code for a total of eight accessory proteins, namely ORFs 3a, 3b, 6, 7a, 7b, 8a, 8b, and 9b. These ORFs are specific for SARS-CoV and do not show significant homology to accessory proteins of other coronaviruses. Structurally, ORF7a possesses a distinctive immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain which is related to extracellular metazoan Ig domains that are involved in adhesion, such as ICAM; it also contains a 15-aa signal peptide sequence at its N terminus, an 81-aa luminal domain, a 21-aa transmembrane domain, and a short C-terminal tail. Coexpression of SARS-CoV ORF7a with S, M, N, and E proteins resulted in production of virus-like particles (VLPs) carrying ORF7a protein, indicating that ORF7a is a viral structural protein. Expression studies of ORF7a have shown that biological functions include induction of apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway, activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, inhibition of host protein translation, and suppression of cell growth progression. These results collectively suggested that ORF7a protein may be involved in virus-host interactions. Pssm-ID: 394935 Cd Length: 121 Bit Score: 216.04 E-value: 3.78e-74
|
|||||||
| bCoV_NS7A | pfam08779 | Betacoronavirus NS7A protein; This entry corresponds to the Human SARS virus NS7A protein ... |
16-121 | 1.52e-64 | |||
Betacoronavirus NS7A protein; This entry corresponds to the Human SARS virus NS7A protein (also known as 7a, accessory protein 7a, X4 and U122). The structure of this protein shows similarities to the immunoglobulin like fold and a known member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) domain superfamily, which suggests a binding activity to integrin I domains. In SARS-CoV-infected cells, the NS7A protein is expressed and retained intra-cellularly within the Golgi network. NS7A has been implicated to function during the replication cycle of SARS-CoV. Pssm-ID: 462600 Cd Length: 107 Bit Score: 191.07 E-value: 1.52e-64
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| ORF7a_SARS-CoV-2-like | cd21684 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) structural accessory protein ... |
1-121 | 3.78e-74 | |||
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) structural accessory protein ORF7a and a bat coronavirus (BatCoV RaTG13) from related betacoronaviruses in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (B lineage); This group contains the structural accessory protein ORF7a, also called NS7a, of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronaviruses (SARS-CoV) from betacoronavirus subgenera Sarbecovirus (lineage B), including SARS-CoV-2, also known as 2019-nCoV, and a bat coronavirus (BatCoV RaTG13), which was previously detected in Rhinolophus affinis from China's Yunnan province. ORF7a/NS7a from betacoronavirus in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (B lineage) are not related to NS7a proteins from other coronavirus lineages. There are five essential genes in CoVs that result in the following gene products: Spike (S) protein, Membrane (M) glycoprotein, Nucleocapsid (N), Envelope (E) protein, and the ORF1ab (a large polyprotein known as replicase/protease); all required to produce a structurally complete viral particle. In addition, SARS-CoV contains a number of open reading frames that code for a total of eight accessory proteins, namely ORFs 3a, 3b, 6, 7a, 7b, 8a, 8b, and 9b. These ORFs are specific for SARS-CoV and do not show significant homology to accessory proteins of other coronaviruses. Structurally, ORF7a possesses a distinctive immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain which is related to extracellular metazoan Ig domains that are involved in adhesion, such as ICAM; it also contains a 15-aa signal peptide sequence at its N terminus, an 81-aa luminal domain, a 21-aa transmembrane domain, and a short C-terminal tail. Coexpression of SARS-CoV ORF7a with S, M, N, and E proteins resulted in production of virus-like particles (VLPs) carrying ORF7a protein, indicating that ORF7a is a viral structural protein. Expression studies of ORF7a have shown that biological functions include induction of apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway, activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, inhibition of host protein translation, and suppression of cell growth progression. These results collectively suggested that ORF7a protein may be involved in virus-host interactions. Pssm-ID: 394935 Cd Length: 121 Bit Score: 216.04 E-value: 3.78e-74
|
|||||||
| bCoV_NS7A | pfam08779 | Betacoronavirus NS7A protein; This entry corresponds to the Human SARS virus NS7A protein ... |
16-121 | 1.52e-64 | |||
Betacoronavirus NS7A protein; This entry corresponds to the Human SARS virus NS7A protein (also known as 7a, accessory protein 7a, X4 and U122). The structure of this protein shows similarities to the immunoglobulin like fold and a known member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) domain superfamily, which suggests a binding activity to integrin I domains. In SARS-CoV-infected cells, the NS7A protein is expressed and retained intra-cellularly within the Golgi network. NS7A has been implicated to function during the replication cycle of SARS-CoV. Pssm-ID: 462600 Cd Length: 107 Bit Score: 191.07 E-value: 1.52e-64
|
|||||||
| ORF7a_SARS-CoV-like | cd21663 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) structural accessory protein ORF7a ... |
14-95 | 2.86e-57 | |||
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) structural accessory protein ORF7a and similar proteins from related betacoronaviruses in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (B lineage); This family contains the structural accessory protein ORF7a, also called NS7a, of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronaviruses (SARS-CoVs) from betacoronavirus subgenera Sarbecovirus (lineage B), including SARS-CoV-2, also known as 2019-nCoV, and a bat coronavirus (BatCoV RaTG13), which was previously detected in Rhinolophus affinis from China's Yunnan province, as well as SARS-related virus from Rhinolophus bats in Europe and Kenya. ORF7a/NS7a from betacoronavirus in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (lineage B) are not related to NS7a proteins from other coronavirus lineages. There are five essential genes in CoVs that result in the following gene products: Spike (S) protein, Membrane (M) glycoprotein, Nucleocapsid (N), Envelope (E) protein, and the ORF1ab (a large polyprotein known as replicase/protease); all required to produce a structurally complete viral particle. In addition, SARS-CoV contains a number of open reading frames that code for a total of eight accessory proteins, namely ORFs 3a, 3b, 6, 7a, 7b, 8a, 8b, and 9b. These ORFs are specific for SARS-CoV and do not show significant homology to accessory proteins of other coronaviruses. Structurally, ORF7a possesses a distinctive immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain which is related to extracellular metazoan Ig domains that are involved in adhesion, such as ICAM; it also contains a 15-amino acid signal peptide sequence at its N terminus, an 81-amino acid luminal domain, a 21-amino acid transmembrane domain, and a short C-terminal tail. Co-expression of SARS-CoV ORF7a with S, M, N and E proteins resulted in production of virus-like particles (VLPs) carrying ORF7a protein, indicating that ORF7a is a viral structural protein. Expression studies of ORF7a have shown that biological functions include induction of apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway, activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, inhibition of host protein translation, and suppression of cell growth progression. These results collectively suggested that ORF7a protein may be involved in virus-host interactions. Pssm-ID: 394934 Cd Length: 83 Bit Score: 172.08 E-value: 2.86e-57
|
|||||||
| ORF7a_SARS-CoV-like | cd21685 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) structural accessory protein ORF7a ... |
14-95 | 1.90e-54 | |||
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) structural accessory protein ORF7a and similar proteins from betacoronaviruses in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (B lineage); This group contains the structural accessory protein ORF7a, also called NS7a, of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronaviruses (SARS-CoVs) from betacoronavirus subgenera Sarbecovirus (lineage B). ORF7a/NS7a from betacoronavirus in the subgenera Sarbecovirus (B lineage) are not related to NS7a proteins from other coronavirus lineages. There are five essential genes in CoVs that result in the following gene products: Spike (S) protein, Membrane (M) glycoprotein, Nucleocapsid (N), Envelope (E) protein, and the ORF1ab (a large polyprotein known as replicase/protease); all required to produce a structurally complete viral particle. In addition, SARS-CoV contains a number of open reading frames that code for a total of eight accessory proteins, namely ORFs 3a, 3b, 6, 7a, 7b, 8a, 8b, and 9b. These ORFs are specific for SARS-CoV and do not show significant homology to accessory proteins of other coronaviruses. Structurally, ORF7a possesses a distinctive immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain which is related to extracellular metazoan Ig domains that are involved in adhesion, such as ICAM; it also contains a 15-aa signal peptide sequence at its N terminus, an 81-aa luminal domain, a 21-aa transmembrane domain, and a short C-terminal tail. Coexpression of SARS-CoV ORF7a with S, M, N, and E proteins resulted in production of virus-like particles (VLPs) carrying ORF7a protein, indicating that ORF7a is a viral structural protein. Expression studies of ORF7a have shown that biological functions include induction of apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway, activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, inhibition of host protein translation, and suppression of cell growth progression. These results collectively suggested that ORF7a protein may be involved in virus-host interactions. Pssm-ID: 394936 Cd Length: 83 Bit Score: 164.87 E-value: 1.90e-54
|
|||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|