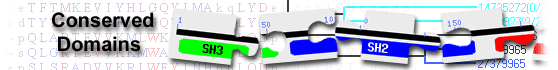
nsp9 [Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2]
List of domain hits

| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| betaCoV_Nsp9 | cd21898 | betacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 ... |
1-113 | 5.27e-65 | |||
betacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 (Nsp9) from betacoronaviruses including highly pathogenic Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV), SARS-CoV2 (also called 2019 novel CoV or 2019-nCoV), and Middle East respiratory syndrome-related (MERS) CoV. CoVs utilize a multi-subunit replication/transcription machinery assembled from a set of non-structural proteins (Nsps) generated as cleavage products of the ORF1a and ORF1ab viral polyproteins. All of these Nsps, except for Nsp1 and Nsp2, are considered essential for transcription, replication, and translation of the viral RNA. Nsp9, with Nsp7, Nsp8, and Nsp10, localizes within the replication complex. Nsp9 is an essential single-stranded RNA-binding protein for coronavirus replication; it shares structural similarity to the oligosaccharide-binding (OB) fold, which is characteristic of proteins that bind to ssDNA or ssRNA. Nsp9 requires dimerization for binding and orienting RNA for subsequent use by the replicase machinery. CoV Nsp9s have diverse forms of dimerization that promote their biological function, which may help elucidate the mechanism underlying CoVs replication and contribute to the development of antiviral drugs. Generally, dimers are formed via interaction of the parallel alpha-helices containing the protein-protein interaction motif GXXXG; additionally, the N-finger region may also play a critical role in dimerization as seen in porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) Nsp9. As a member of the replication complex, Nsp9 may not have a specific RNA-binding sequence but may act in conjunction with other Nsps as a processivity factor, as shown by mutation studies indicating that Nsp9 is a key ingredient that intimately engages other proteins in the replicase complex to mediate efficient virus transcription and replication. : Pssm-ID: 409331 Cd Length: 111 Bit Score: 191.84 E-value: 5.27e-65
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| betaCoV_Nsp9 | cd21898 | betacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 ... |
1-113 | 5.27e-65 | |||
betacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 (Nsp9) from betacoronaviruses including highly pathogenic Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV), SARS-CoV2 (also called 2019 novel CoV or 2019-nCoV), and Middle East respiratory syndrome-related (MERS) CoV. CoVs utilize a multi-subunit replication/transcription machinery assembled from a set of non-structural proteins (Nsps) generated as cleavage products of the ORF1a and ORF1ab viral polyproteins. All of these Nsps, except for Nsp1 and Nsp2, are considered essential for transcription, replication, and translation of the viral RNA. Nsp9, with Nsp7, Nsp8, and Nsp10, localizes within the replication complex. Nsp9 is an essential single-stranded RNA-binding protein for coronavirus replication; it shares structural similarity to the oligosaccharide-binding (OB) fold, which is characteristic of proteins that bind to ssDNA or ssRNA. Nsp9 requires dimerization for binding and orienting RNA for subsequent use by the replicase machinery. CoV Nsp9s have diverse forms of dimerization that promote their biological function, which may help elucidate the mechanism underlying CoVs replication and contribute to the development of antiviral drugs. Generally, dimers are formed via interaction of the parallel alpha-helices containing the protein-protein interaction motif GXXXG; additionally, the N-finger region may also play a critical role in dimerization as seen in porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) Nsp9. As a member of the replication complex, Nsp9 may not have a specific RNA-binding sequence but may act in conjunction with other Nsps as a processivity factor, as shown by mutation studies indicating that Nsp9 is a key ingredient that intimately engages other proteins in the replicase complex to mediate efficient virus transcription and replication. Pssm-ID: 409331 Cd Length: 111 Bit Score: 191.84 E-value: 5.27e-65
|
|||||||
| CoV_NSP9 | pfam08710 | Coronavirus replicase NSP9; Nsp9 is a single-stranded RNA-binding viral protein involved in ... |
1-113 | 5.12e-62 | |||
Coronavirus replicase NSP9; Nsp9 is a single-stranded RNA-binding viral protein involved in RNA synthesis. Several crystallographic structures of nsp9 have shown that it is composed of seven beta strands and a single alpha helix. Nsp9 proteins have N-finger motifs and highly conserved GXXXG motifs that both play critical roles in dimerization. The conserved helix-helix dimer interface containing a GXXXG protein-protein interaction motif is biologically relevant to SARS-CoV replication. Pssm-ID: 285872 Cd Length: 111 Bit Score: 184.60 E-value: 5.12e-62
|
|||||||
| Name | Accession | Description | Interval | E-value | |||
| betaCoV_Nsp9 | cd21898 | betacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 ... |
1-113 | 5.27e-65 | |||
betacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 (Nsp9) from betacoronaviruses including highly pathogenic Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV), SARS-CoV2 (also called 2019 novel CoV or 2019-nCoV), and Middle East respiratory syndrome-related (MERS) CoV. CoVs utilize a multi-subunit replication/transcription machinery assembled from a set of non-structural proteins (Nsps) generated as cleavage products of the ORF1a and ORF1ab viral polyproteins. All of these Nsps, except for Nsp1 and Nsp2, are considered essential for transcription, replication, and translation of the viral RNA. Nsp9, with Nsp7, Nsp8, and Nsp10, localizes within the replication complex. Nsp9 is an essential single-stranded RNA-binding protein for coronavirus replication; it shares structural similarity to the oligosaccharide-binding (OB) fold, which is characteristic of proteins that bind to ssDNA or ssRNA. Nsp9 requires dimerization for binding and orienting RNA for subsequent use by the replicase machinery. CoV Nsp9s have diverse forms of dimerization that promote their biological function, which may help elucidate the mechanism underlying CoVs replication and contribute to the development of antiviral drugs. Generally, dimers are formed via interaction of the parallel alpha-helices containing the protein-protein interaction motif GXXXG; additionally, the N-finger region may also play a critical role in dimerization as seen in porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) Nsp9. As a member of the replication complex, Nsp9 may not have a specific RNA-binding sequence but may act in conjunction with other Nsps as a processivity factor, as shown by mutation studies indicating that Nsp9 is a key ingredient that intimately engages other proteins in the replicase complex to mediate efficient virus transcription and replication. Pssm-ID: 409331 Cd Length: 111 Bit Score: 191.84 E-value: 5.27e-65
|
|||||||
| CoV_Nsp9 | cd21881 | coronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 (Nsp9) ... |
1-113 | 4.24e-62 | |||
coronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 (Nsp9) from coronaviruses, including highly pathogenic betacoronaviruses such as Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV), SARS-CoV2 (also called 2019 novel CoV or 2019-nCoV), and Middle East respiratory syndrome-related (MERS) CoV. CoVs utilize a multi-subunit replication/transcription machinery assembled from a set of non-structural proteins (Nsps) generated as cleavage products of the ORF1a and ORF1ab viral polyproteins. All of these Nsps, except for Nsp1 and Nsp2, are considered essential for transcription, replication, and translation of the viral RNA. Nsp9, with Nsp7, Nsp8, and Nsp10, localizes within the replication complex. Nsp9 is an essential single-stranded RNA-binding protein for CoV replication; it shares structural similarity to the oligosaccharide-binding (OB) fold, which is characteristic of proteins that bind to ssDNA or ssRNA. Nsp9 requires dimerization for binding and orienting RNA for subsequent use by the replicase machinery. CoV Nsp9s have diverse forms of dimerization that promote their biological function, which may help elucidate the mechanism underlying CoVs replication and contribute to the development of antiviral drugs. Generally, dimers are formed via interaction of the parallel alpha-helices containing the protein-protein interaction motif GXXXG at the C-terminus; additionally, the N-finger region may also play a critical role in dimerization as seen in porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) Nsp9. As a member of the replication complex, Nsp9 may not have a specific RNA-binding sequence but may act in conjunction with other Nsps as a processivity factor, as shown by mutation studies indicating that Nsp9 is a key ingredient that intimately engages other proteins in the replicase complex to mediate efficient virus transcription and replication. Pssm-ID: 409329 Cd Length: 111 Bit Score: 184.64 E-value: 4.24e-62
|
|||||||
| CoV_NSP9 | pfam08710 | Coronavirus replicase NSP9; Nsp9 is a single-stranded RNA-binding viral protein involved in ... |
1-113 | 5.12e-62 | |||
Coronavirus replicase NSP9; Nsp9 is a single-stranded RNA-binding viral protein involved in RNA synthesis. Several crystallographic structures of nsp9 have shown that it is composed of seven beta strands and a single alpha helix. Nsp9 proteins have N-finger motifs and highly conserved GXXXG motifs that both play critical roles in dimerization. The conserved helix-helix dimer interface containing a GXXXG protein-protein interaction motif is biologically relevant to SARS-CoV replication. Pssm-ID: 285872 Cd Length: 111 Bit Score: 184.60 E-value: 5.12e-62
|
|||||||
| alphaCoV_Nsp9 | cd21897 | alphacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 ... |
1-113 | 3.43e-35 | |||
alphacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 (Nsp9) of alphacoronaviruses, including Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV), Porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus (TGEV), and Human coronavirus 229E. CoVs utilize a multi-subunit replication/transcription machinery assembled from a set of non-structural proteins (Nsps) generated as cleavage products of the ORF1a and ORF1ab viral polyproteins. All of these Nsps, except for Nsp1 and Nsp2, are considered essential for transcription, replication, and translation of the viral RNA. Nsp9, with Nsp7, Nsp8, and Nsp10, localizes within the replication complex. Nsp9 is an essential single-stranded RNA-binding protein for coronavirus replication; it shares structural similarity to the oligosaccharide-binding (OB) fold, which is characteristic of proteins that bind to ssDNA or ssRNA. Nsp9 requires dimerization for binding and orienting RNA for subsequent use by the replicase machinery. CoV Nsp9s have diverse forms of dimerization that promote their biological function, which may help elucidate the mechanism underlying CoVs replication and contribute to the development of antiviral drugs. Generally, dimers are formed via interaction of the parallel alpha-helices containing the protein-protein interaction motif GXXXG; additionally, the N-finger region may also play a critical role in dimerization as seen in porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) Nsp9. As a member of the replication complex, Nsp9 may not have a specific RNA-binding sequence but may act in conjunction with other Nsps as a processivity factor, as shown by mutation studies indicating that Nsp9 is a key ingredient that intimately engages other proteins in the replicase complex to mediate efficient virus transcription and replication. Pssm-ID: 409330 Cd Length: 108 Bit Score: 116.65 E-value: 3.43e-35
|
|||||||
| gammaCoV_Nsp9 | cd21899 | gammacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 ... |
1-113 | 5.29e-26 | |||
gammacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 (Nsp9) from gammacoronaviruses such as Avian infectious bronchitis virus (IBV). CoVs utilize a multi-subunit replication/transcription machinery assembled from a set of non-structural proteins (Nsps) generated as cleavage products of the ORF1a and ORF1ab viral polyproteins. All of these Nsps, except for Nsp1 and Nsp2, are considered essential for transcription, replication, and translation of the viral RNA. Nsp9, with Nsp7, Nsp8, and Nsp10, localizes within the replication complex. Nsp9 is an essential single-stranded RNA-binding protein for coronavirus replication; it shares structural similarity to the oligosaccharide-binding (OB) fold, which is characteristic of proteins that bind to ssDNA or ssRNA. Nsp9 requires dimerization for binding and orienting RNA for subsequent use by the replicase machinery. CoV Nsp9s have diverse forms of dimerization that promote their biological function, which may help elucidate the mechanism underlying CoVs replication and contribute to the development of antiviral drugs. Generally, dimers are formed via interaction of the parallel alpha-helices containing the protein-protein interaction motif GXXXG; additionally, the N-finger region may also play a critical role in dimerization as seen in porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) Nsp9. As a member of the replication complex, Nsp9 may not have a specific RNA-binding sequence but may act in conjunction with other Nsps as a processivity factor, as shown by mutation studies indicating that Nsp9 is a key ingredient that intimately engages other proteins in the replicase complex to mediate efficient virus transcription and replication. Pssm-ID: 409332 Cd Length: 113 Bit Score: 93.38 E-value: 5.29e-26
|
|||||||
| deltaCoV_Nsp9 | cd21900 | deltacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 ... |
1-113 | 1.16e-18 | |||
deltacoronavirus non-structural protein 9; This model represents the non-structural protein 9 (Nsp9) from deltacoronaviruses such as the Porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) Porcine coronavirus HKU15. CoVs utilize a multi-subunit replication/transcription machinery assembled from a set of non-structural proteins (Nsps) generated as cleavage products of the ORF1a and ORF1ab viral polyproteins. All of these Nsps, except for Nsp1 and Nsp2, are considered essential for transcription, replication, and translation of the viral RNA. Nsp9, with Nsp7, Nsp8, and Nsp10, localizes within the replication complex. Nsp9 is an essential single-stranded RNA-binding protein for coronavirus replication; it shares structural similarity to the oligosaccharide-binding (OB) fold, which is characteristic of proteins that bind to ssDNA or ssRNA. Nsp9 requires dimerization for binding and orienting RNA for subsequent use by the replicase machinery. CoV Nsp9s have diverse forms of dimerization that promote their biological function, which may help elucidate the mechanism underlying CoVs replication and contribute to the development of antiviral drugs. Generally, dimers are formed via interaction of the parallel alpha-helices containing the protein-protein interaction motif GXXXG; additionally, the N-finger region may also play a critical role in dimerization as seen in porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) Nsp9. As a member of the replication complex, Nsp9 may not have a specific RNA-binding sequence but may act in conjunction with other Nsps as a processivity factor, as shown by mutation studies indicating that Nsp9 is a key ingredient that intimately engages other proteins in the replicase complex to mediate efficient virus transcription and replication. Pssm-ID: 409333 Cd Length: 109 Bit Score: 74.39 E-value: 1.16e-18
|
|||||||
| Blast search parameters | ||||
|